What is COSHH?
COSHH stands for “Control of Substances Hazardous to Health.” It is a set of regulations in the United Kingdom that require employers to control harmful substances. COSHH regulations are intended to safeguard workers from the risks connected with job exposure to hazardous substances.
Rules and regulations compel businesses to assess risks, manage exposure, and provide employees with information and training on the hazards and proper handling of certain substances.
Understanding The Hazard Groups
The Control of Substances Hazardous to Health (COSHH) regulations categorizes hazardous substances into nine main groups based on their potential risks to health. These groups include substances that are harmful to health through inhalation, such as dusts, vapors, gases, and fumes. Inhalation hazards can arise from various sources, including chemical processes, manufacturing operations, or certain types of work environments like construction sites or laboratories. Employers must implement measures to control the release of these substances into the air and provide appropriate respiratory protection to workers to minimize the risk of exposure.
Another significant COSHH hazard group encompasses substances that can cause skin irritation, sensitization, or corrosion. These substances include chemicals like acids, alkalis, solvents, and certain types of oils. Skin exposure to these hazardous substances can lead to various health issues ranging from mild irritation to severe burns or allergic reactions. Employers are required to implement measures such as providing personal protective equipment (PPE), establishing safe handling procedures, and ensuring proper training to minimize the risk of skin exposure and mitigate the potential health hazards associated with these substances.
While the HSE website shows pictograms here, we provide a much more in depth guide to each hazard group.
Below we will give a brief overview and background into each of the hazard groups and how to identify them.
Explosive
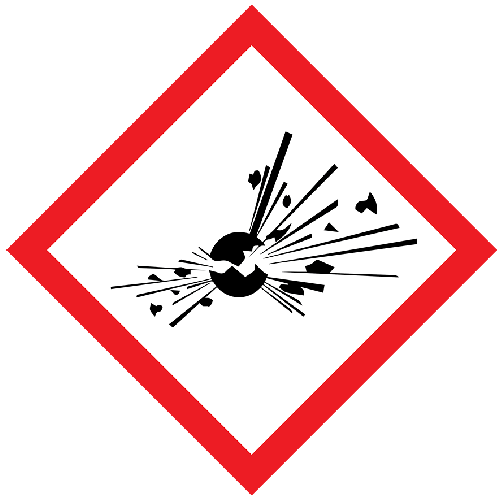

When ignited, explosive compounds can rapidly release energy in the form of heat, light, sound, or pressure. These compounds represent considerable risks to occupational health and safety because they have the potential to cause serious injuries, fatalities, and property damage.
Employers must follow tight regulations for handling, storing, and transporting explosive material in order to reduce the danger of accidents or incidents. Proper risk assessments, safe handling procedures, enough training, and the deployment of appropriate control mechanisms are required to guarantee that explosive substances are managed safely in compliance with COSHH recommendations.
Flammable

Flammable substances within the framework of COSHH (Control of Substances Hazardous to Health) regulations in the workplace encompass a broad spectrum of materials capable of catching fire and sustaining combustion when exposed to an ignition source. These hazards include liquids, gases, and solids with varying degrees of flammability. Common examples of flammable substances encountered in workplaces include volatile solvents, such as paints, varnishes, and cleaning agents, which can emit flammable vapors.
Additionally, gases like propane, methane, and hydrogen present flammability risks, especially in industrial settings where they may be used for heating or as fuel sources. Solid materials such as wood dust, certain metals, and finely powdered chemicals can also pose flammability hazards, particularly when dispersed in the air as dust clouds.
Understanding the properties and risks associated with these flammable substances is crucial for employers to implement effective control measures and ensure the safety of workers in accordance with COSHH guidelines.
Oxidising

Oxidising substances refer to materials capable of releasing oxygen or other oxidising agents, thereby promoting the combustion of other substances. These hazards encompass a diverse array of chemicals and compounds that can react vigorously with combustible materials, potentially leading to fires or explosions if not handled properly.
Common examples of oxidising substances encountered in workplaces include hydrogen peroxide, chlorine bleach, and nitric acid, which are frequently used in cleaning, disinfection, and industrial processes. Also, certain organic peroxides and perchlorates are classified as oxidising substances due to their ability to decompose rapidly, releasing oxygen and heat.
Corrosive
Corrosive substances are materials capable of causing severe damage to living tissue upon contact, including skin, eyes, and mucous membranes, as well as corroding materials such as metals.
These hazards encompass a wide range of chemicals with acidic, alkaline, or other corrosive properties. Common examples of corrosive substances encountered in workplaces include strong acids like sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and nitric acid, which are often used in manufacturing processes, laboratories, and cleaning applications.
Strong alkaline substances such as sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide pose corrosive hazards, particularly in industries like metal processing and chemical manufacturing
Toxic

Toxic substances are materials capable of causing harm to human health through various routes of exposure, including inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact.
These hazards encompass a wide range of chemicals and compounds with toxic properties, including carcinogens, mutagens, reproductive toxins, and substances with acute or chronic toxicity.
Some examples of toxic substances encountered in workplaces include heavy metals such as lead, mercury, and cadmium, which can cause neurological damage, organ failure, and other serious health effects. Hazardous chemicals like formaldehyde, benzene, and asbestos pose toxic risks, potentially leading to respiratory problems, cancer, and other adverse health outcomes
Hazardous To The Environment
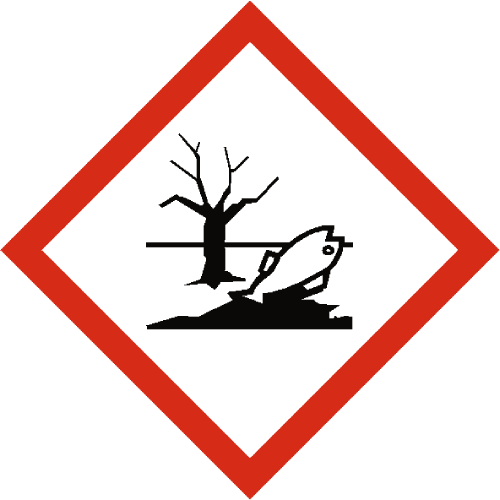

Environmental hazards within the COSHH (Control of Substances Hazardous to Health) regulations in the workplace pertain to substances that can pose risks not only to human health but also to the surrounding environment.
These hazards include chemicals and materials that have the potential to contaminate air, water, soil, and ecosystems, leading to adverse effects on plants, animals, and the overall ecological balance.
Examples of environmental hazards encountered in workplaces encompass pollutants such as heavy metals, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), pesticides, and persistent organic pollutants (POPs), which can accumulate in the environment and have long-lasting impacts on ecosystems and biodiversity.
Hazardous waste materials generated from industrial processes, manufacturing operations, and research activities pose environmental risks if not properly managed and disposed of according to regulations. Implementing effective control measures, waste management practices, and pollution prevention strategies are essential for minimizing the environmental footprint of workplaces and ensuring compliance with COSHH guidelines.
Health Hazard / Hazard To The O-Zone

Hazardous to the ozone layer substances within the COSHH regulations are chemicals known to deplete the Earth’s ozone layer, which shields the planet from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), halons, and other ozone-depleting substances (ODS) are examples of such hazardous materials. These substances are commonly found in refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and fire extinguishing agents. When released into the atmosphere, ODS molecules rise to the stratosphere where they undergo photodissociation, releasing chlorine and bromine atoms. These atoms catalytically destroy ozone molecules, leading to the formation of the ozone hole and increasing the risk of harmful UV radiation reaching the Earth’s surface. The regulation of ODS under COSHH involves strict controls on their production, use, and disposal, aiming to mitigate their environmental impact and safeguard the Earth’s ozone layer.
These substances are also general health hazards that can cause respiratory issues, or other non fatal and serious problems.
Serious Health Hazard
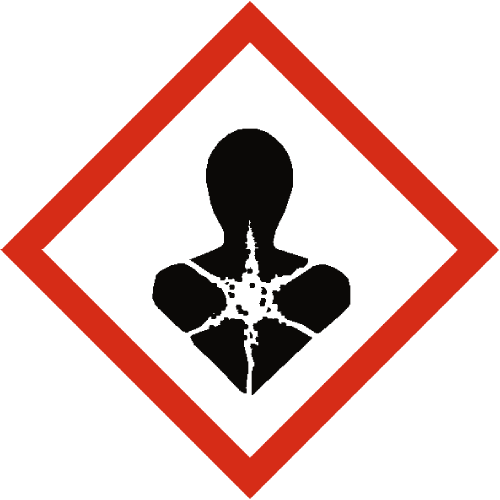

A serious health hazard within the COSHH regulations in the workplace encompasses substances capable of causing severe harm to human health through exposure.
These hazards include a broad range of chemicals and materials with toxic, carcinogenic, mutagenic, or otherwise harmful properties. Examples of serious health hazards encountered in workplaces include asbestos fibres, which can cause lung cancer, mesothelioma, and asbestosis upon inhalation.
Certain chemicals like benzene, formaldehyde, and lead pose serious health risks, including neurological damage, respiratory problems, and organ failure, with prolonged or high-level exposure.
Gas Under Pressure
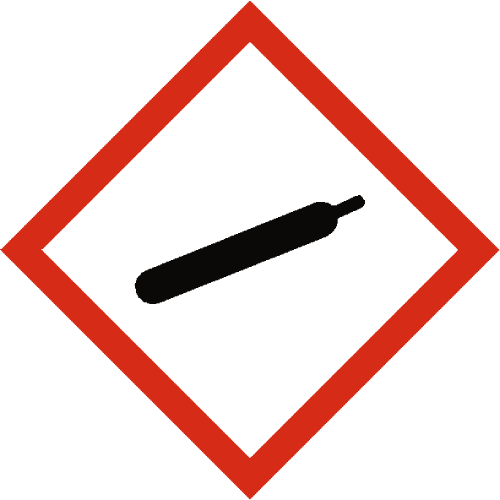

Gas under pressure in the workplace refers to substances stored or used in pressurized containers, which can pose significant hazards if mishandled or released.
These hazards encompass compressed gases, liquefied gases, and dissolved gases stored at high pressures, presenting risks such as explosions, ruptures, and asphyxiation.
Common examples of gas under pressure hazards encountered in workplaces include compressed air cylinders used for pneumatic tools, acetylene cylinders for welding and cutting operations, and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) cylinders for heating and cooking purposes. Improper handling, storage, or transportation of pressurized gas containers can result in catastrophic accidents, leading to injuries, fatalities, and property damage.
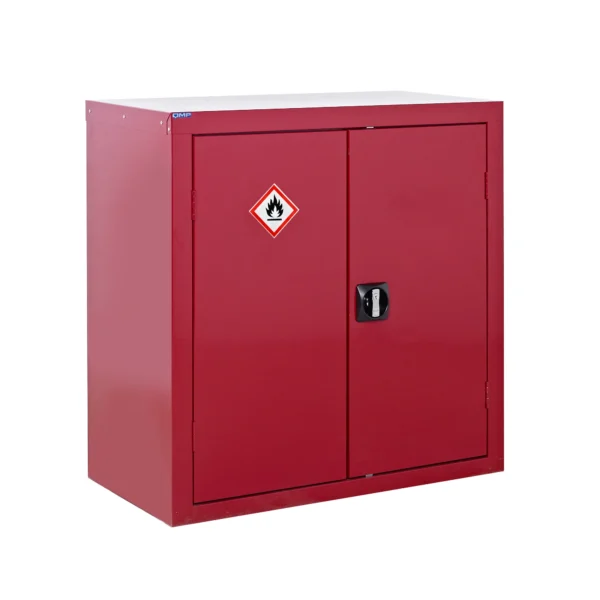
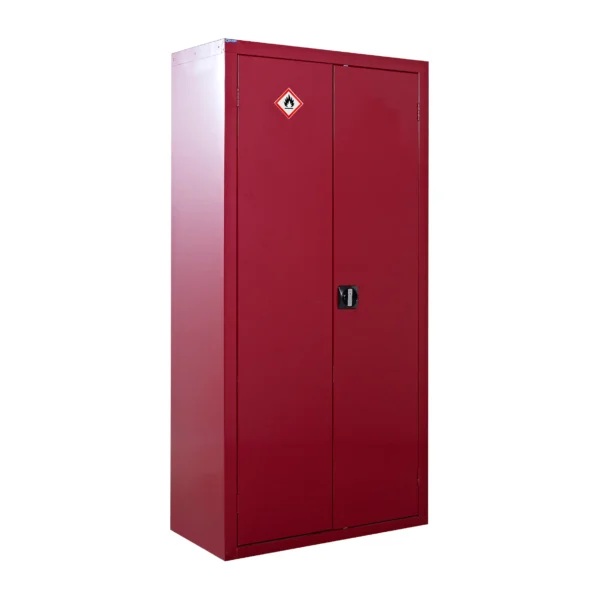
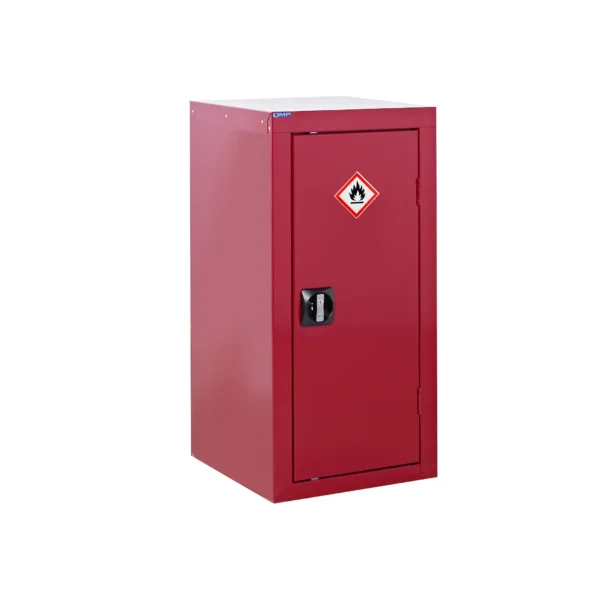
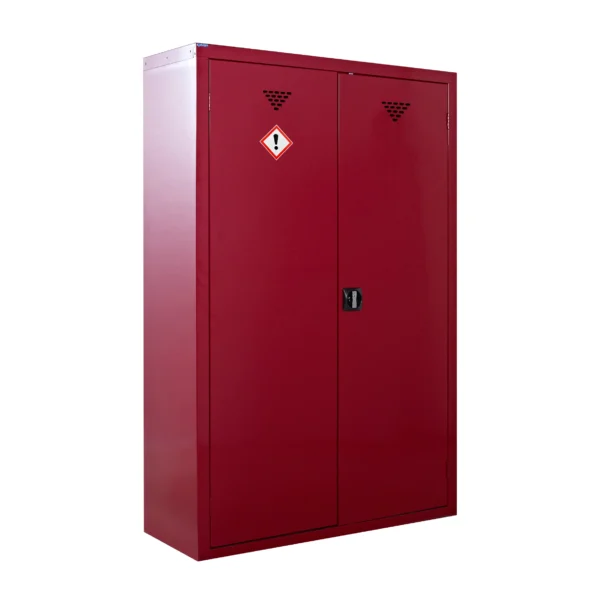
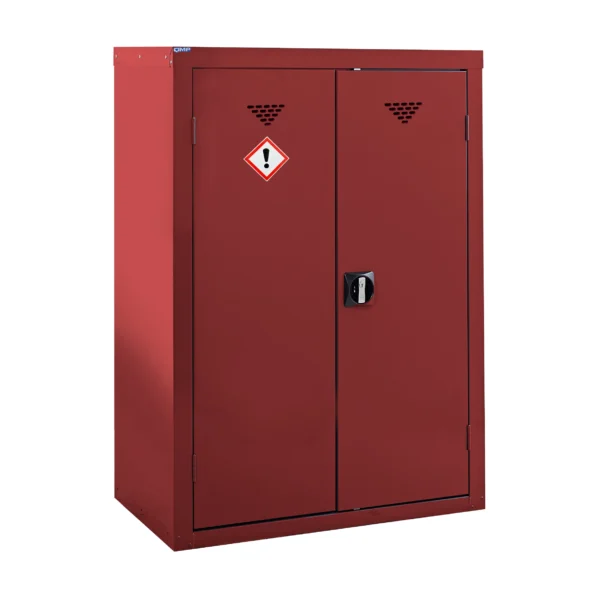
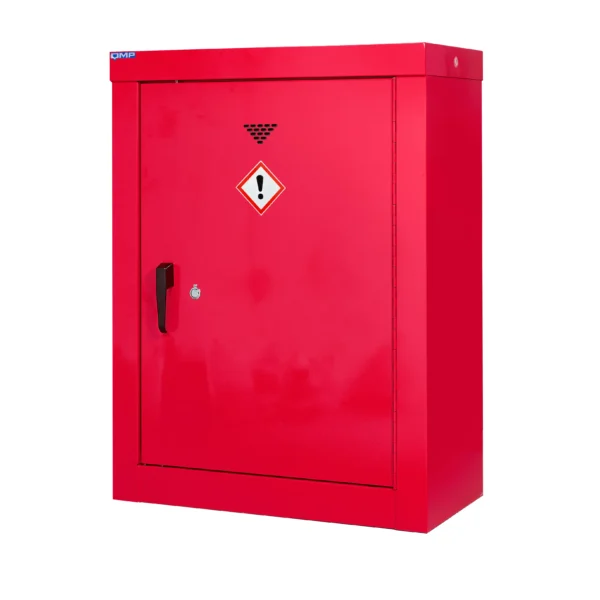
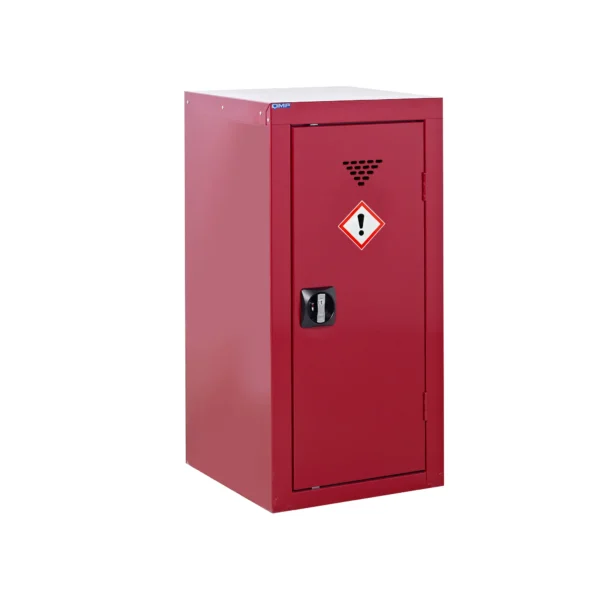
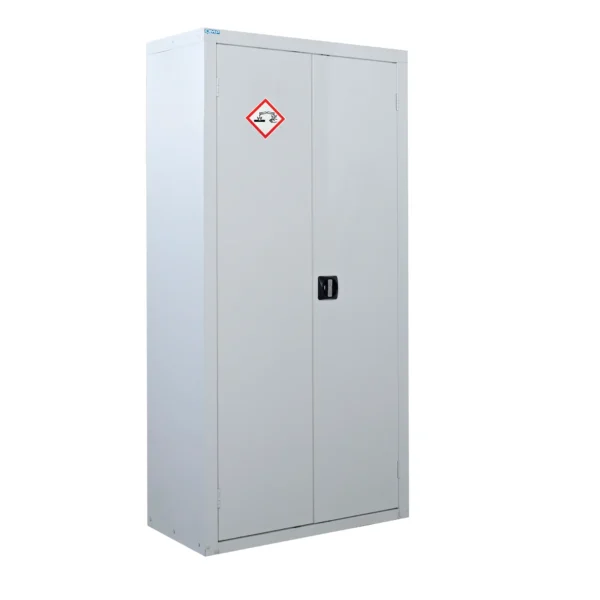
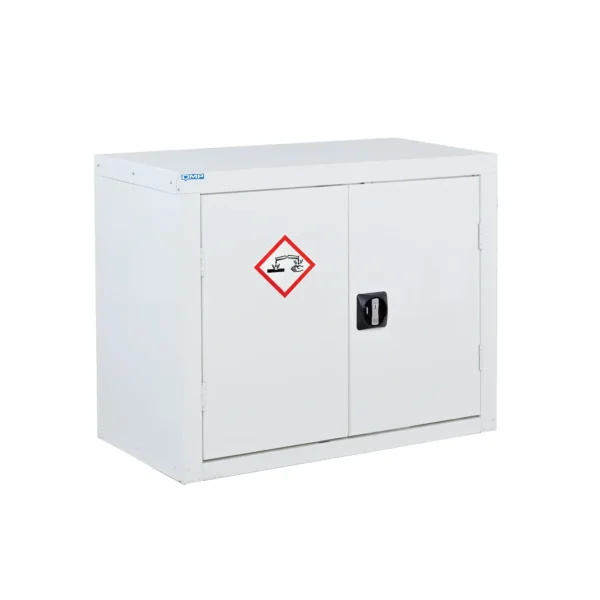
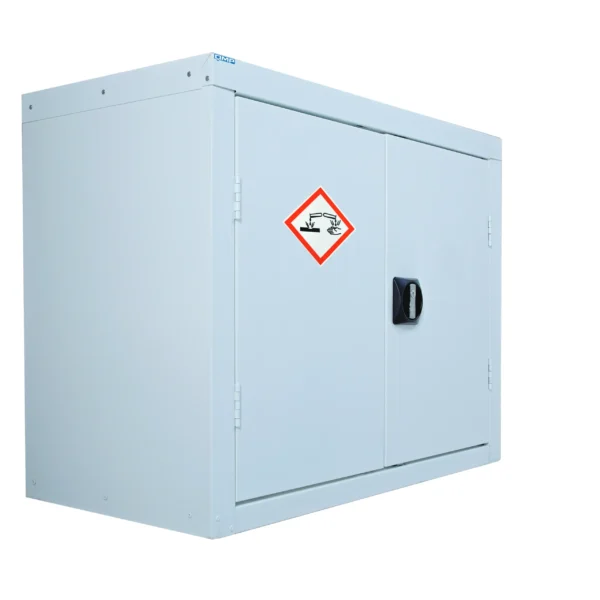
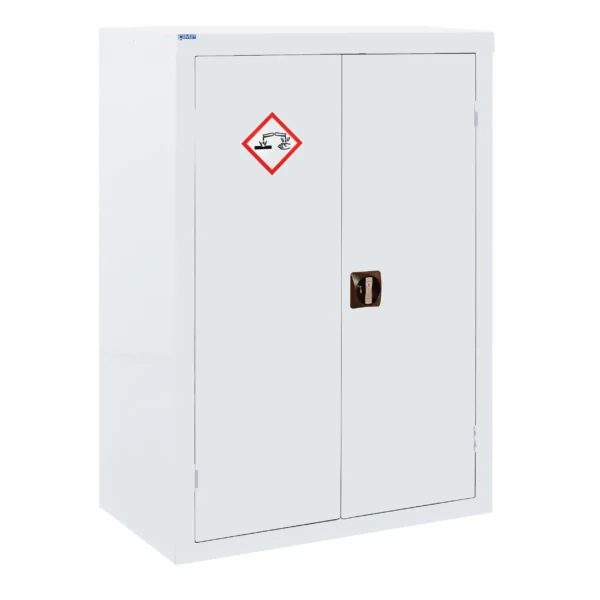
A COSHH cabinet, also known as a hazardous substance storage cabinet or chemical storage cabinet, is a specialized storage unit designed to safely store hazardous substances in the workplace in compliance with COSHH regulations.
These cabinets are typically constructed from robust materials such as steel and feature secure locking mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access.
COSHH cabinets are designed to segregate and organize hazardous materials based on their properties, such as flammability, toxicity, or corrosiveness, to minimize the risk of accidental exposure or contamination.
They often include features such as spill containment trays, ventilation systems, and warning labels to enhance safety.
Using COSHH cabinets helps employers ensure proper storage and handling of hazardous substances, reducing the risk of accidents, injuries, and environmental contamination in the workplace.
-
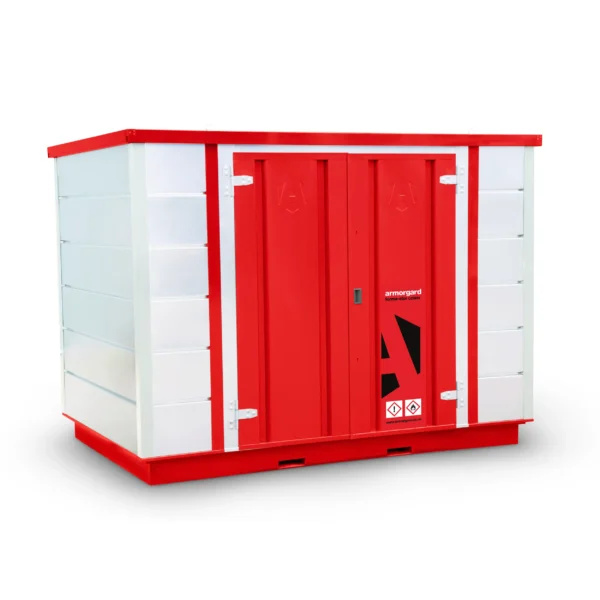
Armorgard Forma-Stor COSHH – FR300-C
From £5,575.11 Ex. VAT Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
COSHH Colour Coding – Which One Is Right?
In many workplaces, COSHH cabinets are colour-coded to facilitate easy identification of the types of hazardous substances stored within them. While colour coding may vary slightly depending on regional regulations or workplace standards, the following colour scheme is commonly used:
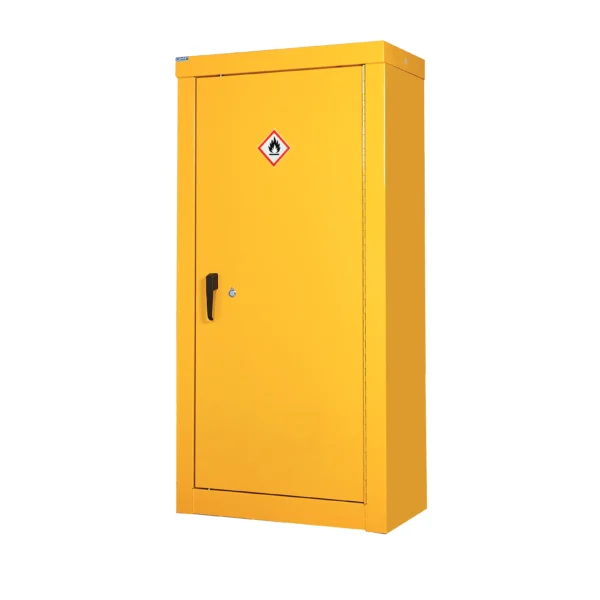
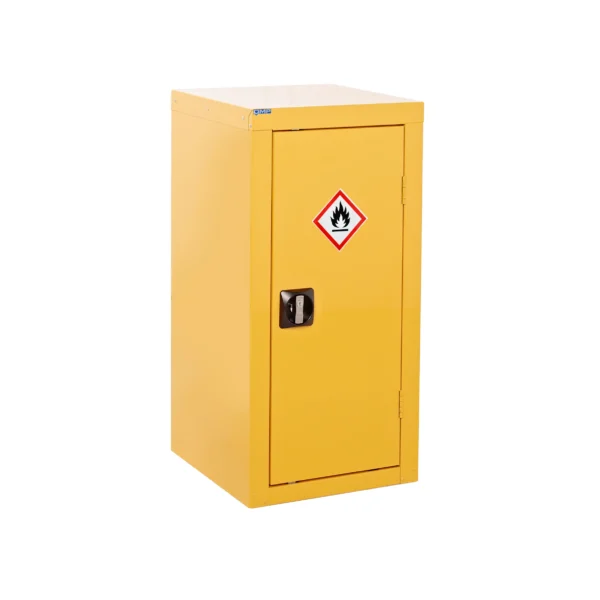
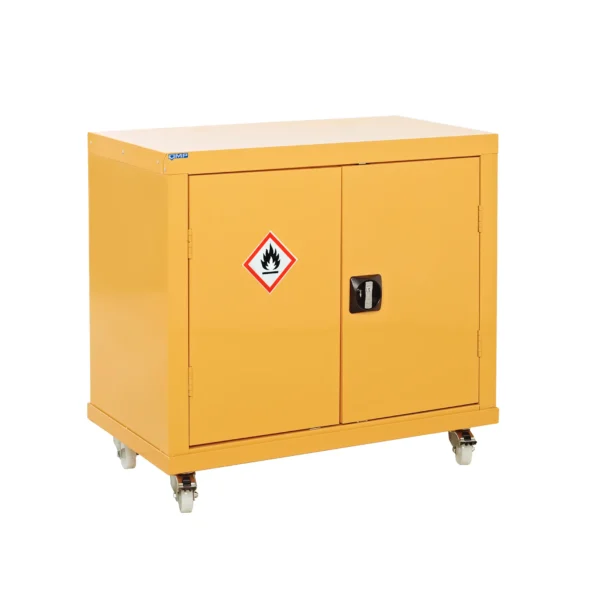
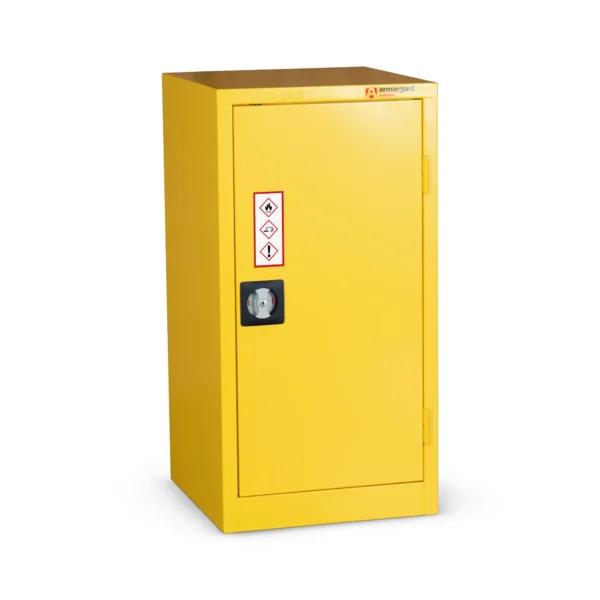
Yellow: Cabinets with yellow doors full yellow carcass typically indicate the storage of flammable materials, such as solvents, fuels, or certain chemicals prone to combustion.
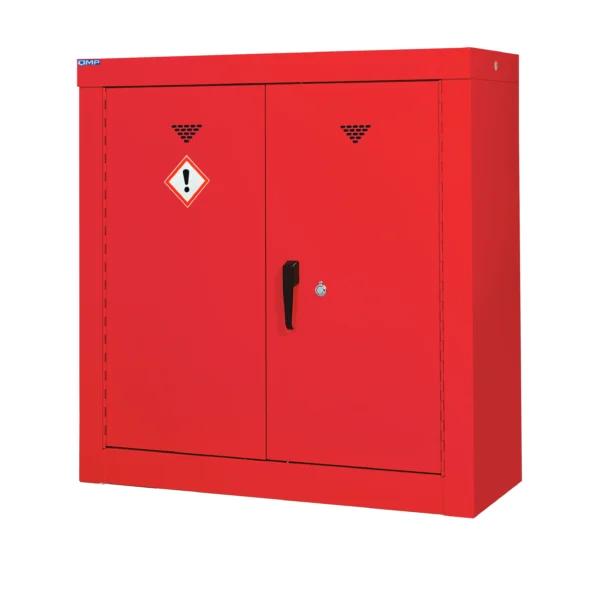
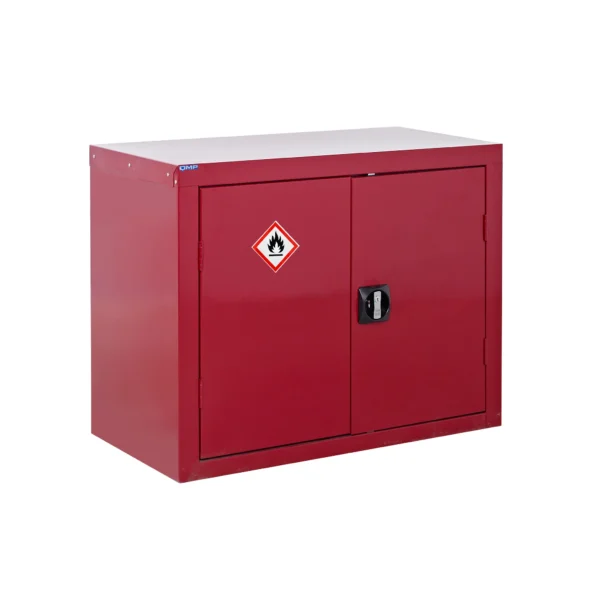
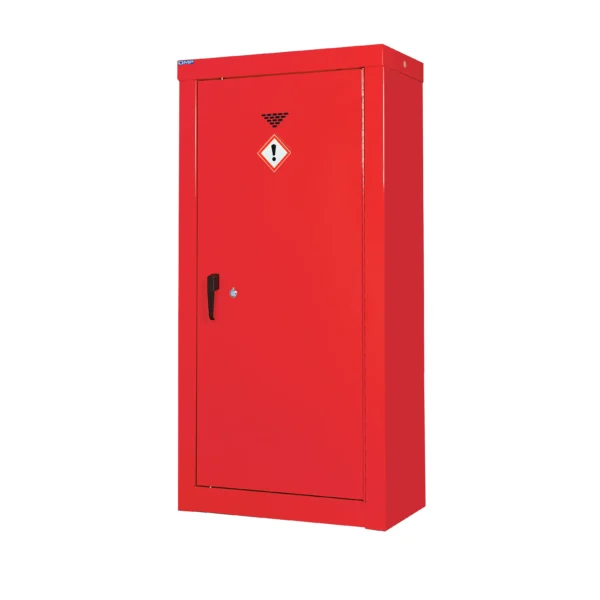
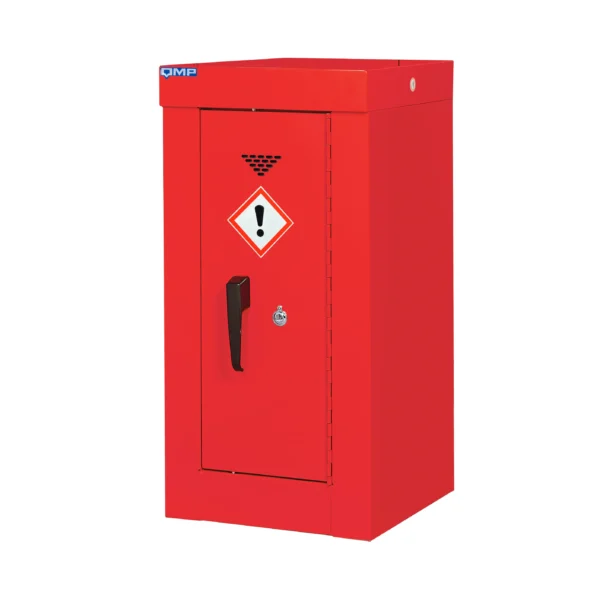
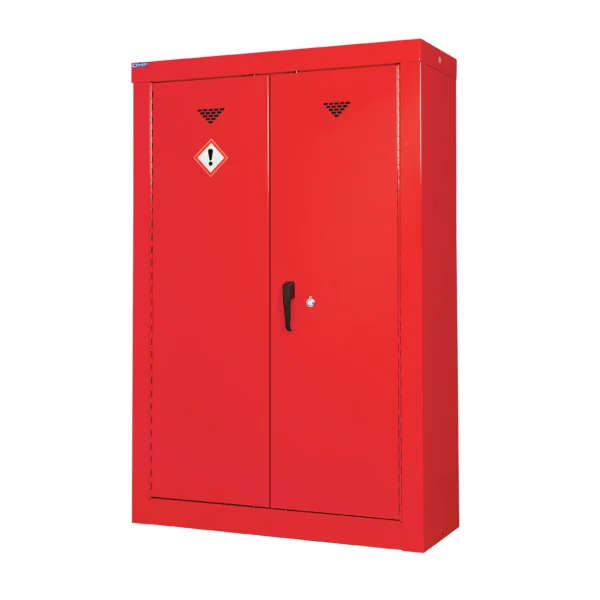
Red: Cabinets with red doors or full colour carcasses are commonly used for storing substances that pose a risk to health, such as chemicals.
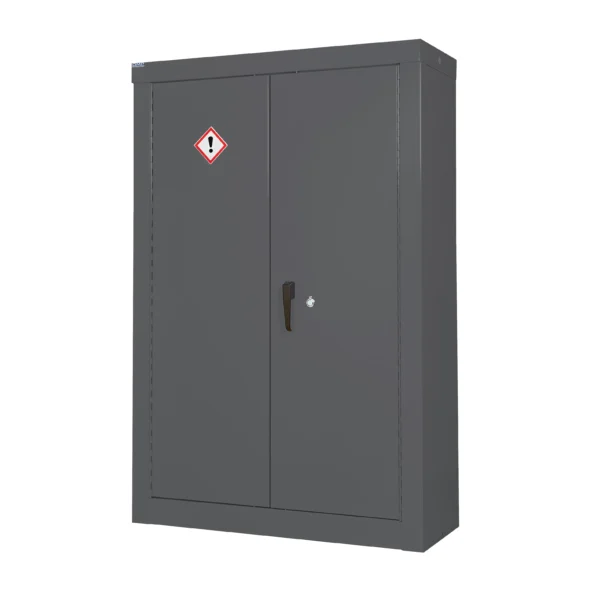
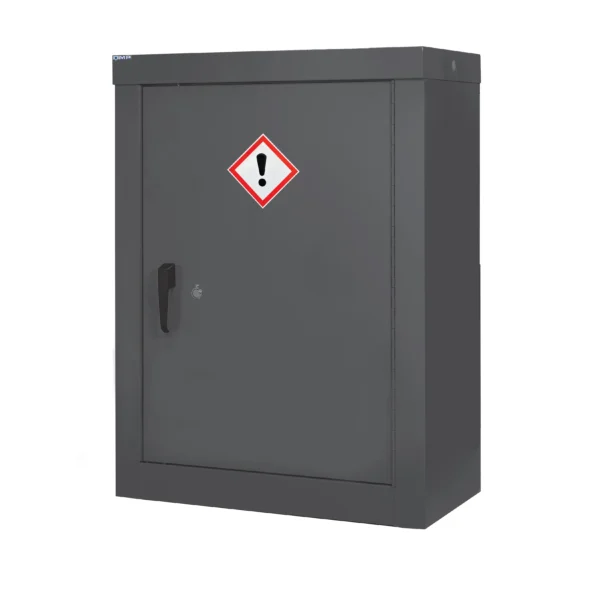
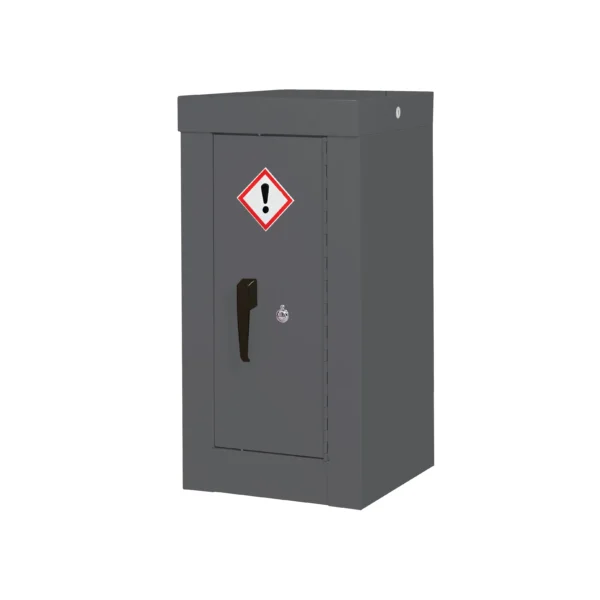
Grey: Some workplaces may use grey cabinets for general storage purposes or for substances that do not fit into the other color-coded categories. These can also be for cleaning compounds and those that are hazardous to general health and the o-zone.
Green: Cabinets with green doors or labels are generally used for storing pesticides, insecticides or other substances that are harmful to the environment.
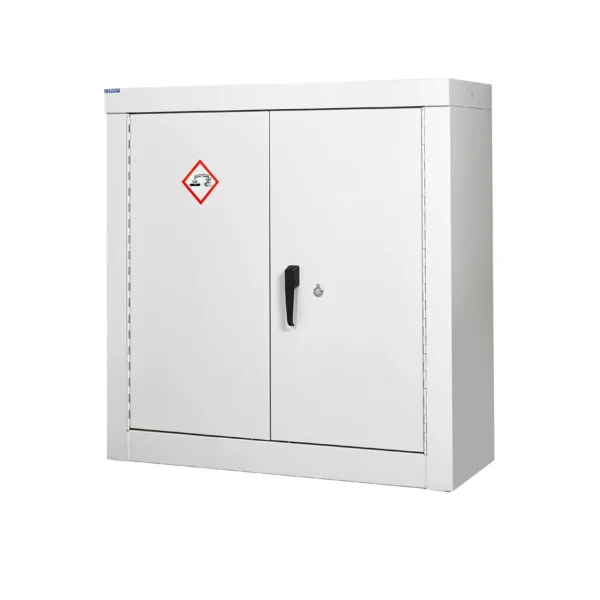
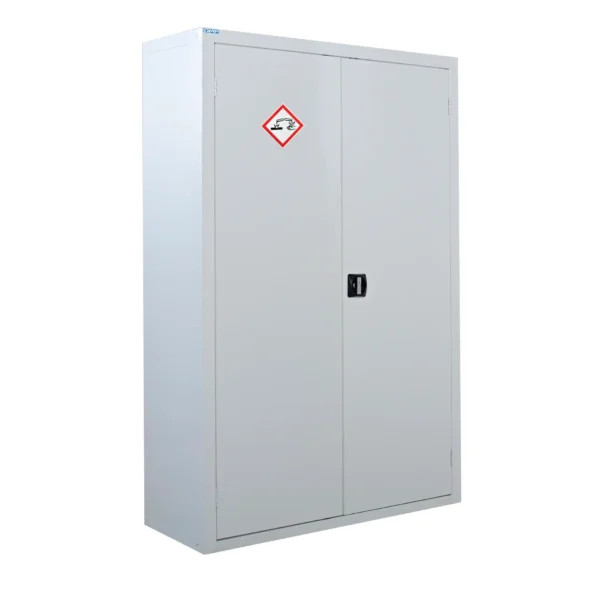
White: White cabinets are those for corrosive compounds that need to be stored away from all other chemicals. Acids and Alkalis are stored in separate White cabinets.
It’s important to note that while these colour codes are widely used and recognized, they may not be universal, and employers should always ensure that their color-coding system aligns with relevant regulations and guidelines to maintain safety standards in the workplace.
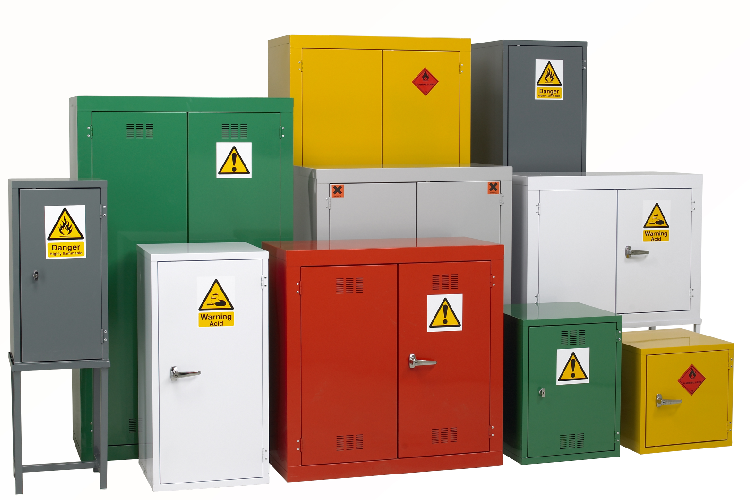

Types of COSHH Cabinets
COSHH cabinets are specialized storage units designed to safely store hazardous substances in the workplace, and they are typically categorized based on the types of hazardous materials they are intended to contain. Here are five common types of COSHH cabinets:
Flammable COSHH cabinets are essential safety equipment in workplaces where flammable liquids are handled or stored.
These cabinets are specially designed to provide secure storage for substances that pose a risk of combustion or fire. Constructed with fire-resistant materials and equipped with features like ventilation systems, flammable cabinets are crucial for minimizing the risk of ignition and containing fires should they occur. Typically identifiable by their bright yellow color, these cabinets adhere to strict safety standards and regulations to ensure the protection of both workers and the workplace environment.
Examples of items commonly stored in flammable COSHH cabinets include various types of solvents, fuels, paints, adhesives, and aerosols. Flammable liquids such as acetone, ethanol, and gasoline are frequently stored in these cabinets due to their inherent combustible properties.
Products like paints, varnishes, adhesives, and aerosols contain volatile compounds that can ignite easily, making them suitable candidates for storage within flammable cabinets. By securely housing these hazardous materials, flammable COSHH cabinets play a critical role in mitigating the risk of fires and ensuring workplace safety.
General hazardous COSHH cabinets serve as versatile storage solutions in workplaces where a variety of hazardous materials need to be stored safely.
These cabinets are designed to accommodate a wide range of substances that may pose risks to health and safety but do not fall under specific categories like flammable or corrosive materials.
Constructed from durable materials and often featuring adjustable shelving and secure locking mechanisms, general item hazardous COSHH cabinets help organizations comply with safety regulations and maintain a tidy and organized workspace. They are typically identifiable by their labelling and are usually Grey in colour.
Examples of items commonly stored in general item hazardous COSHH cabinets include various chemical products such as cleaning agents, solvents, and pesticides that may have multiple hazards associated with them.
These cabinets may also house smaller quantities of flammable or corrosive substances alongside other hazardous materials. Items like batteries, fluorescent light bulbs, and electronic waste containing hazardous components such as heavy metals or toxic chemicals may be stored in general item hazardous COSHH cabinets to prevent environmental contamination and ensure safe disposal.
-
Armorgard SafeStor – HFC4
From £290.66 Ex. VAT Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Chemical storage COSHH cabinets are purpose-built units designed to safely house various hazardous chemicals in workplaces.
These cabinets are constructed from durable materials such as steel and are equipped with features like adjustable shelving, ventilation systems, and secure locking mechanisms to ensure the safe storage of chemicals.
Chemical storage cabinets play a crucial role in minimizing the risk of accidental exposure, spills, and contamination, thereby protecting both workers and the environment. They are often prominently labeled and may be color-coded usually red to facilitate easy identification and organization of different types of chemicals.
Pesticide and insecticide COSHH cabinets are specialized storage units designed to securely house various types of pesticides, insecticides, and other agricultural chemicals.
These cabinets are constructed from durable materials and equipped with features such as adjustable shelving, ventilation systems, and secure locking mechanisms to ensure the safe storage of hazardous chemicals used in pest control and agriculture.
Pesticide and insecticide COSHH cabinets play a crucial role in minimizing the risk of accidental exposure, spills, and environmental contamination associated with these chemicals. They are typically labelled prominently and may be color-coded green to facilitate easy identification and organization of different types of pesticides and insecticides.
Examples of items commonly stored in pesticide and insecticide COSHH cabinets include various formulations of pesticides and insecticides used for agricultural purposes, pest control, and weed management. These may include liquid concentrates, powders, granules, and aerosol sprays containing active ingredients such as organophosphates, pyrethroids, neonicotinoids, and herbicides
Corrosive chemical COSHH cabinets are specialized storage units designed to safely house corrosive substances such as acids, bases, and other chemicals that can cause damage to living tissue upon contact and corrode materials like metals.
These cabinets are equipped with features like spill containment trays, ventilation systems, and secure locking mechanisms.
Corrosive chemical COSHH cabinets play a crucial role in minimizing the risk of accidental exposure, spills, and damage associated with these hazardous chemicals in the workplace. They are typically prominently labeled and may be color-coded white.
In the workplace, corrosive chemical COSHH cabinets are used to store a wide range of corrosive materials used in various industrial processes, laboratories, and manufacturing operations. Things stored in these include strong acids like sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid, as well as bases such as sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide.
What To Look For When Buying COSHH Cabinets
Here at HSE Store we aim to provide only the very best on the market, long term durability and the stand out solution for any application.
Heavy Duty Construction
COSHH cabinets should be constructed with heavy duty use in mind, as they can be frequently accessed by employees on a daily basis and used for storing strong and heavy liquids or chemicals.
All of our cabinets we have here at HSE Store are for heavy duty use, and constructed from 20swg steel or above.
We only supply cabinets from British manufacturers, as they have fulfilled every need that a workplace should have when purchasing COSHH cabinets, with no corners cut.
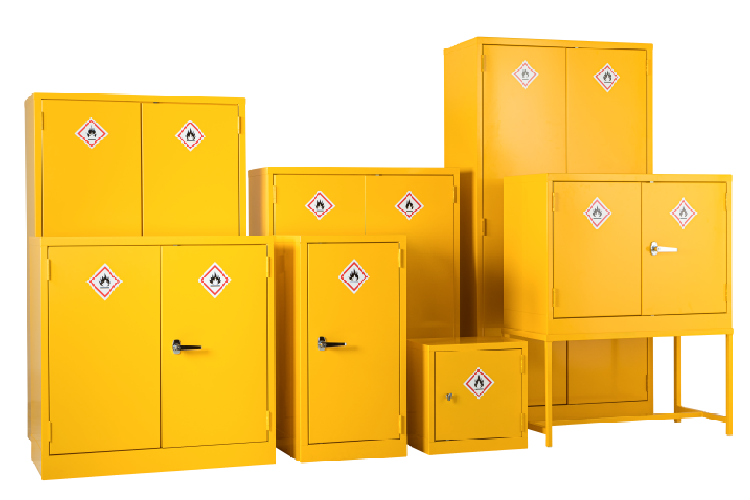

Locking Doors
COSHH cabinets should be lockable to prevent unauthorized access to hazardous substances stored within them. Lockable cabinets help control and restrict access to dangerous materials, ensuring that only authorized personnel who have received proper training and are equipped with necessary personal protective equipment (PPE) are able to handle or use hazardous substances.
Our Redditek cabinets are all secure locking lever lock handles, with 2 rods top and bottom, 2 keys included and have reinforced construction.
Our green pesticide and red chemical cabinets are also ventilated to prevent the build up of gases and fumes.

Colour Coding
COSHH cabinets are often colour-coded to facilitate easy identification and organization of hazardous substances stored within them. Colour coding helps quickly convey information about the types of hazards associated with the materials contained in the cabinets, enhancing safety measures in the workplace.
All of our COSHH cabinets are not just colour coded in terms of their doors, but the full carcass. If needed we can also quote for additional colours that we don’t offer as standard to match your existing company policy.

Proven Manufacture
Any COSHH cabinets that you look for on the market can initially look well in pictures. However one thing you should be focused on from a business and safety point of view is the longevity and proven manufacture of these safety cabinets.
Drawing on a manufacturing capability that spans over 45 years, Redditek cabinets have a team that is made up of skilled experts who are passionate about their craft and take genuine pride in their work. Blending this craftsmanship with innovations in technology such as our state-of-the-art laser cutter, robotic arm, powder coating facility and CAD, they design, create and construct products at the forefront of safety, quality and durability standards.
It is this length of time in creating safety products that you can trust Redditek to fulfil your requirements to a high standard, and built right here in Britain.

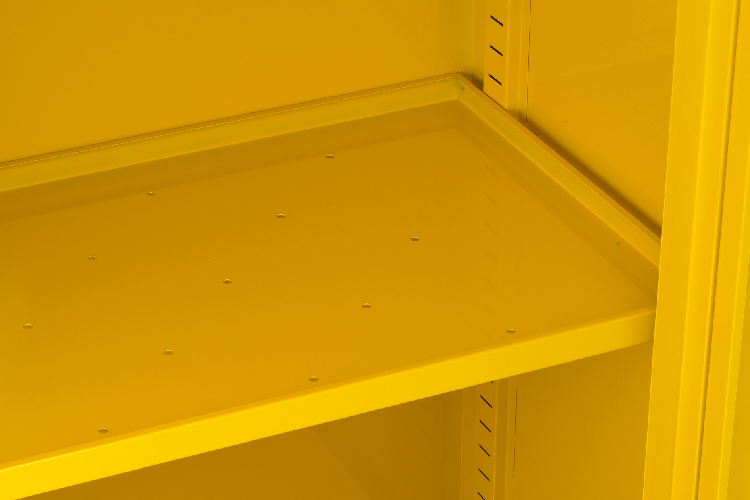
Shelving
COSHH cabinets are usually provided with multiple shelves for storing products. This is essential as COSHH items and chemicals can come in various sizes and quantities, and also some may need to be stored above or below other products.
Adjustable shelves like the ones we supply are important to allow you to restructure your storage requirements on a 25mm pitch.
Not only this, but the stand out feature (which should be common-place yet it isn’t across all manufacturers), is the punched shelving that allows for drainage of spilled chemicals directly into the sump below.

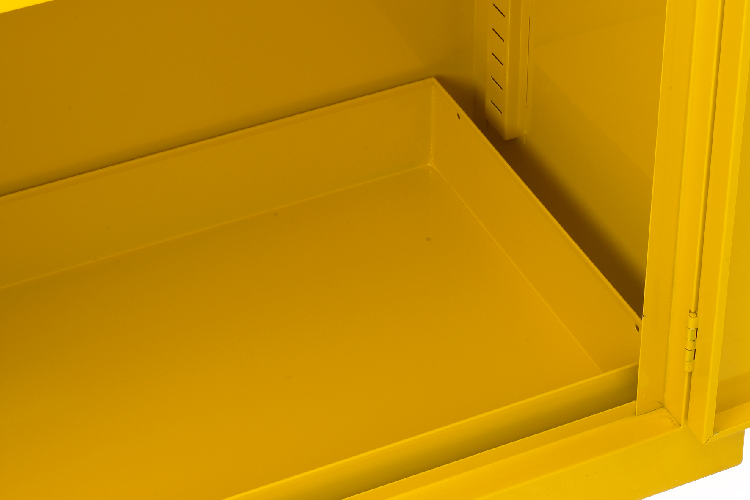
Sump Trays & Capacity
Sumps are essential components of COSHH cabinets because they serve as a containment measure for any spills, leaks, or drips that may occur from the hazardous substances stored within the cabinets.
The presence of a sump helps prevent any spilled liquids from escaping the cabinet and spreading onto the floor or surrounding areas, thereby minimizing the risk of environmental contamination and exposure to hazardous materials.
Sumps are typically integrated into the base of COSHH cabinets and are designed to capture and retain liquids, allowing for easy cleanup and disposal.
Our Redditek cabinets feature a removable sump for easy cleaning and maintenance work, especially useful for allowing employees to clean safely without being exposed to harmful fumes for long periods.

FAQ's
What Is The Colour Code For COSHH Cabinets?
- Yellow for flammables
- Red for chemicals
- Grey for general hazard or mixed chemicals
- White for corrosives such as acid and alkali
- Green for pesticides and insecticides
What Does COSHH Cover In The Workplace?
COSHH, which stands for Control of Substances Hazardous to Health, covers a wide range of hazardous substances in the workplace. These substances include chemicals, products, and materials that have the potential to cause harm to human health through various routes of exposure, such as inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact.
COSHH regulations apply to both substances that are directly hazardous to health and those that may pose indirect risks, such as substances that can generate harmful fumes or dust during use.
What Is The Golden Rule For COSHH?
The “golden rule” for COSHH is to prevent or control exposure to hazardous substances as much as reasonably practicable.
This principle emphasizes the importance of taking proactive measures to minimize the risk of harm to workers’ health from exposure to hazardous substances in the workplace.
It entails identifying potential hazards, assessing the risks associated with those hazards, implementing effective control measures to eliminate or minimize exposure, and regularly reviewing and updating safety procedures to ensure ongoing protection.
What Are Examples Of A COSHH Hazard?
Examples of COSHH (Control of Substances Hazardous to Health) hazards include:
-
Chemical Hazards: Substances such as acids, solvents, cleaning agents, pesticides, and laboratory chemicals can pose risks to health through inhalation, skin contact, or ingestion. These substances may cause irritation, allergic reactions, or more serious health effects such as respiratory problems, organ damage, or cancer.
-
Biological Hazards: Biological agents such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and certain allergens can pose health risks in environments such as healthcare settings, laboratories, or agricultural workplaces. Exposure to biological hazards may result in infections, allergic reactions, or other adverse health effects.
-
Dust Hazards: Dust particles generated during activities such as woodworking, construction, or manufacturing processes can pose respiratory hazards. Examples include wood dust, silica dust, asbestos fibres, and metal dusts, which may cause lung diseases such as asthma, silicosis, or asbestos-related diseases.
-
Flammable and Explosive Hazards: Flammable liquids, gases, and vapours present risks of fire and explosion if not properly controlled. Examples include fuels, solvents, and gases such as propane or hydrogen. These substances may ignite easily, leading to fires, explosions, or thermal burns.
There are many more examples, but this is just a few.
Who Is Responsible For COSHH?
The employer is responsible for COSHH at the workplace.
This means that they must ensure all relevant activities and equipment are compliant with the COSHH regulations.
COSHH is a legal requirement for employers to adhere to.
Employees however must also follow the guidelines and adhere to company practices and policies.
What Is The First Thing You Do For COSHH?
The first thing must be to identify the hazard.
What Are The COSHH Symbols?
 – Gas Under Pressure
– Gas Under Pressure
 – Health hazard/Hazardous to the ozone layer
– Health hazard/Hazardous to the ozone layer
 – Hazardous to the environment
– Hazardous to the environment
 – Acute toxicity
– Acute toxicity
 – Corrosive
– Corrosive
 – Oxidising
– Oxidising
 – Explosive
– Explosive
 – Flammable
– Flammable
 – Serious Health Hazard
– Serious Health Hazard
What Does COSHH Stand For?
Control Of Substances Hazardous To Health
Final Thoughts
We hope that you enjoyed reading our guide, it should be very engaging and something to think about very carefully from a health and safety point of view while at the same time a revenue increasing investment for your business.
We only supply the best top quality safety equipment here at HSE Store that is manufactured right here in Britain.
For further reading, see the rest of our knowledge base articles by clicking here.
Alternatively you can view the official HSE guidance on COSHH here
You can view the entire range of our COSHH Cabinets by clicking below.












































































































































































































